16 Tenses In English Grammar Pdf Books

16 Tenses In English Grammar Tense membahas perubahan bentuk kata kerja (verb) sesuai dengan waktu terjadinya suatu. Peristiwa serta kesempurnaan kejadiannya Unsur tense: Unsur tense: 1. Perubahan verb; 2. Waktu terjadinya; 3. Kesempurnaan peritiwa. Perubahan verb; Present verb 1 Past verb 2 Past. All Tenses: Fill in the correct form. When we reach Land's End we. (not start, give). I put the five-pound notes into one of the books; but the next day it. (see, paint, you like). The car had nobody I it but the engine.
The Paper 16 Tenses English • 1. FACULTY OF TEACHER TRAINIG AND EDUCATION ENGLISH LANGUAGE UNIVERSITY RIAU KEPULAUAN (UNRIKA) 2014-2015 THE PAPER READING II Compiled By: Complete name: Ririn Febriyanti N.P.M: 14.06.0.047 Topic: 16 Tenses in English • PROLOGUE The author praises and thanksgiving pray Allah SWT for all His mercy and grace so that authors can complete a paper for English course work, entitled '16 ENGLISH tenses' just in time. The author would like to thank all those who have helped to motivate and give useful suggestions that authors can make this paper as well. In particular, authors thank for the lecturer Reading II in English who has been given the task of this paper. There by increasing knowledge about the author that there are 16 tenses in English. In this paper I will discuss about the various and use of tenses in English.
Tenses is the syntax. As we know, tenses are important in learning English, or the use of English in all respects.
Therefore I would like to discuss about the tenses so that we better understand about the tenses, so we did not err in applying the English language. Like the Indonesian language, we must consider the use of tenses in a sentence.
What should we say if you make a sentence which we do, we're doing, and we will do. In English, the pattern of negative and positive sentences are different, there is the addition of the words in the pattern of negative sentences. Not much different from Indonesian, English only more specific in the use of the word. Okay, let's start discussing about the tenses. The author realized that the paper is still far from perfect, for that author expects criticism and constructive suggestions for the perfection of this paper. Hopefully this paper is particularly useful to readers and fellow students in general.
Batam, April 8th, 2015 Ririn Febriyanti 2 • CONTENTS PROLOGUE.................. 2 CHAPTER I......................4 ENGLISH TENSE SYSTEM............... 4 I.1 English Tense System................4 I.2 What is Tense?................5 TENSE (NOUN) IS A FORM OF A VERB USED TO INDICATE THE TIME, AND SOMETIMES THE CONTINUATION OR COMPLETENESS, OF AN ACTION IN RELATION TO THE TIME OF SPEAKING. (FROM LATIN TEMPUS = TIME). TENSE IS A METHOD THAT WE USE IN ENGLISH TO REFER TO TIME - PAST, PRESENT AND FUTURE.
MANY LANGUAGES USE TENSES TO TALK ABOUT TIME. OTHER LANGUAGES HAVE NO TENSES, BUT OF COURSE THEY CAN STILL TALK ABOUT TIME, USING DIFFERENT METHODS............... 5 I.3 Tense and Time.................6 I.4 Basic Tenses.................7 I.5 Basic Tenses: Regular Verb...............8 I.6 Basic Tenses: Irregular Verb..............9 THE BASIC STRUCTURE OF TENSES FOR REGULAR VERBS AND IRREGULAR VERBS IS EXACTLY THE SAME (EXCEPT TO BE).
THE ONLY DIFFERENCE IS THAT WITH REGULAR VERBS THE PAST AND PAST PARTICIPLE ARE ALWAYS THE SAME (WORKED, WORKED), WHILE WITH IRREGULAR VERBS THE PAST AND PAST PARTICIPLE ARE NOT ALWAYS THE SAME (SANG, SUNG). BUT THE STRUCTURE IS THE SAME! IT WILL HELP YOU A GREAT DEAL TO REALLY UNDERSTAND THAT.10 I.7 Basic Tenses: Be................11 CHAPTER II......................13 ENGLISH TENSES TIMELINE...............13 a.
Simple Present Tenses...............13 b. Present Continuous /Progressive Tenses............14 c.
Present Perpect Tense...............14 d. Present Perfect Continuous/Progressive............15 e. Simple Past tense................16 f. Countinuous or Progressive Tense.............16 g.
Past Perfect Tenses................17 h. Past Perfect Continuous/Progessive Tense...........17 i.
Future tense.................18 j. Future Continuous/Progressive Tense............18 18 k. Future perfect Tense................19 l. Present Perfect Continuous/Progressive Tense..........20 m. Past Future Tense................20 The Pattern of Past Future Tense..............21 n.
Past Future Continuous Tense..............21 The Pattern of Past Future Continuous Tense...........21 3 • o. Past Future Perfect Tense...............22 The Pattern of Past Future Perfect Tense............22 p. Past Future Perfect Continuous Tense............23 The Pattern of Past Future Perfect Continuous Tense..........23 CHAPTER III.................. 24 EXAMPLE OF 16 TENSES...............24 a. Present Tenses................24 b. Present Continuous/Progressive Tenses............26 c.
Present Perpect Tense...............27 d. Present Continuous/Progressive Tense............28 e. Simple Past Tenses................29 f. Past Countinuous/Progressive Tense.............30 g. Past perfect Tenses................30 h. Past Perfect Countinuous/Progressive Tense...........31 i. Future Tense.................31 j.
Future Continuous/Progressive Tense............32 k. Future Perfect Tense................33 l. Future Perfect Continuous/Progressive Tense...........33 m. Past Future Tense................34 The Pattern of Past Future Tense..............34 n. Past Future Continuous Tense..............34 The Pattern of Past Future Continuous Tense...........34 o. Past Future Perfect Tense...............35 The Pattern of Past Future Perfect Tense............35 p. Past Future Perfect Continuous Tense............35 The Pattern of Past Future Perfect Continuous Tense..........35 CHAPTER IV..................36 REFERENCES.................
37 A HANDBOOK OF ENGLISH GRAMMAR (TATA BAHASA INGGRIS LENGKAP)- OLEH SLAMET RIYANTO, EMILIA NH, LEILA NH..........37 HTTP://WWW.ENGLISHCLUB.COM/GRAMMAR/VERB-TENSES_SYS-WHAT.HTM.37 HTTP://WWW.EGO4U.COM/EN/CRAM-UP/GRAMMAR/TENSES.....37 HTTP://WWW.ENGLISHPAGE.COM/IRREGULARVERBS/IRREGULARVERBS.HTML37 HTTPS://WWW.ENGLISHCLUB.COM/VOCABULARY/REGULAR-VERBS-LIST.HTM.37 CHAPTER I ENGLISH TENSE SYSTEM I.1 English Tense System In some languages, verb tenses are not very important or do not even exist. In English, the concept of tense is very important. 4 • In this lesson we look at the idea behind tense, how to avoid confusing tense with time, and the structure of the basic tenses, with examples using a regular verb, an irregular verb and the verb be.
What is Tense? Tense & Time 3. Basic Tenses 4. Regular Verbs 5.
Irregular Verbs 6. Be I.2 What is Tense?
Tense (noun) is a form of a verb used to indicate the time, and sometimes the continuation or completeness, of an action in relation to the time of speaking. (From Latin tempus = time). Tense is a method that we use in English to refer to time - past, present and future. Many languages use tenses to talk about time. Other languages have no tenses, but of course they can still talk about time, using different methods. So, we talk about time in English with tenses.
But, and this is a very big but: • we can also talk about time without using tenses (for example, going to is a special construction to talk about the future, it is not a tense) • one tense does not always talk about one time (see Tense & Time for more about this) Here are some of the terms used in discussing verbs and tenses: a. Mood Indicative mood expresses a simple statement of fact, which can be positive (affirmative) or negative. • I like coffee. • I do not like coffee.
Interrogative mood expresses a question • Why do you like coffee? Imperative mood expresses a command • Sit down! Subjunctive mood expresses what is imagined or wished or possible • The President ordered that he attend the meeting. Voice 5 • Voice shows the relationship of the subject to the action.
In the active voice, the subject does the action (cats eat mice). In the passive voice, the subject receives the action (mice are eaten by cats). Among other things, we can use voice to help us change the focus of attention. Aspect Aspect expresses a feature of the action related to time, such as completion or duration.
Present simple and past simple tenses have no aspect, but if we wish we can stress with other tenses that: • The action or state referred to by the verb is completed (and often still relevant), For example: I have emailed the report to Jane. (so now she has the report) (This is called perfective aspect, using perfect tenses.) • The action or state referred to by the verb is in progress or continuing (that is, uncompleted), For example: We are eating. (This is called progressive aspect, using progressive [continuous] tenses.) I.3 Tense and Time It is important not to confuse the name of a verb tense with the way we use it to talk about time. For example: a present tense does not always refer to present time: • I hope it rains tomorrow.
'rains' is present simple, but it refers here to future time (tomorrow). Or a past tense does not always refer to past time: • If I had some money now, I could buy it. 'had' is past simple but it refers here to present time (now). The following examples show how different tenses can be used to talk about different times. Tense TIME 6 • Past Present Future Present Simple I want a coffee.
I leave tomorrow. She likes coffee Present Continuous I am having dinner. I am taking my exam next month.
She likes coffee Present Perfect Simple I have seen ET. I have finished. Present Perfect Continuous I have been playing tennis. We have been working for four hours. Past Simple I finished one hour ago.
If she loved you now, she would marry you. If you came tomorrow, you would see her. Past Continuous I was working at 2 am this morning. Past Perfect Simple I had not eaten for 24 hours. Past Perfect Continuous We had been working for 3 hours.
If I had been working now, I would have missed you. If I had been working tomorrow, I could not have agreed.
Future Simple Hold on. I'll do it now. I'll see you tomorrow.
Future Continuous I will be working at 9 pm tonight. Future Perfect Simple I will have finished by 9pm tonight. We will have been married for ten years next month. Future Perfect Continuous They may be tired when you arrive because they will have been working. In 30 minutes, we will have been working for four hours. I.4 Basic Tenses For past and present, there are 2 simple tenses + 6 complex tenses (using auxiliary verbs). To these, we can add 4 'modal tenses' for the future (using modal auxiliary verbs will/shall).
This makes a total of 12 tenses in the active voice. Another 12 tenses are available in the passive voice. So now we have 24 tenses. Emco Msi Package Builder Professional Keygenguru there.
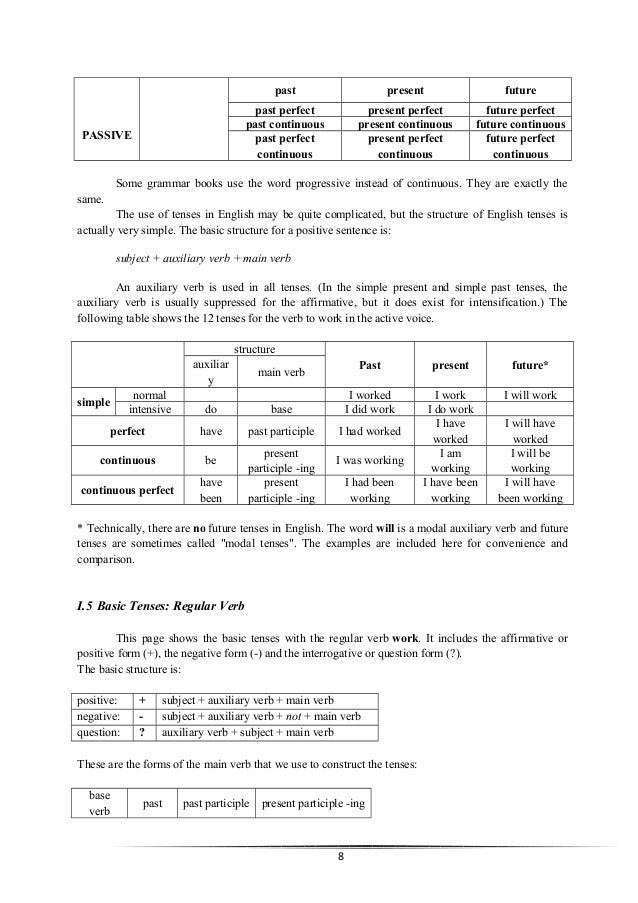
24 Tenses past present future* ACTIVE simple tenses past present future complex tenses formed with auxiliary verbs past perfect present perfect future perfect past continuous present continuous future continuous past perfect continuous present perfect continuous future perfect continuous 7 • PASSIVE past present future past perfect present perfect future perfect past continuous present continuous future continuous past perfect continuous present perfect continuous future perfect continuous Some grammar books use the word progressive instead of continuous. They are exactly the same. The use of tenses in English may be quite complicated, but the structure of English tenses is actually very simple. The basic structure for a positive sentence is: subject + auxiliary verb + main verb An auxiliary verb is used in all tenses. (In the simple present and simple past tenses, the auxiliary verb is usually suppressed for the affirmative, but it does exist for intensification.) The following table shows the 12 tenses for the verb to work in the active voice. Structure Past present future*auxiliar y main verb simple normal I worked I work I will work intensive do base I did work I do work perfect have past participle I had worked I have worked I will have worked continuous be present participle -ing I was working I am working I will be working continuous perfect have been present participle -ing I had been working I have been working I will have been working * Technically, there are no future tenses in English.
The word will is a modal auxiliary verb and future tenses are sometimes called 'modal tenses'. The examples are included here for convenience and comparison. I.5 Basic Tenses: Regular Verb This page shows the basic tenses with the regular verb work. It includes the affirmative or positive form (+), the negative form (-) and the interrogative or question form (?).
The basic structure is: positive: + subject + auxiliary verb + main verb negative: - subject + auxiliary verb + not + main verb question:? Auxiliary verb + subject + main verb These are the forms of the main verb that we use to construct the tenses: base verb past past participle present participle -ing 8 • work worke d worked working past present future SIMPLE do + base verb (except future: will + base verb) + I did work I worked I do work I work I will work - I did not work I do not work I will not work? SIMPLE PERFECT have + past participle + I had worked I have worked I will have worked - I had not worked I have not worked I will not have worked? Had I worked? Have I worked?
Will I have worked? CONTINUOUS be + ing + I was working I am working I will be working - I was not working I am not working I will not be working? Was I working? Am I working?
Will I be working? CONTINUOUS PERFECT have been + ing + I had been working I have been working I will have been working - I had not been working I have not been working I will not have been working? Had I been working? Have I been working? Will I have been working?
I.6 Basic Tenses: Irregular Verb This page shows the basic tenses with the irregular verb sing. It includes the affirmative or positive form (+), the negative form (-) and the interrogative or question form (?). The basic structure is: positive: + subject + auxiliary verb + main verb negative: - subject + auxiliary verb + not + main verb question:? Aj-c2wa-c118 Software Download there.
Auxiliary verb + subject + main verb These are the forms of the main verb that we use to construct the tenses: base verb past past participle present participle -ing Sing sang sung singing past present future SIMPLE do + base + I did sing I sang I do sing I sing I will sing - I did not sing I do not sing I will not sing 9 • verb (except future: will + base verb)? SIMPLE PERFECT have + past participle + I had sung I have sung I will have sung - I had not sung I have not sung I will not have sung? Will I have sung? CONTINUOU S be + -ing + I was singing I am singing I will be singing - I was not singing I am not singing I will not be singing? Was I singing?
Am I singing? Will I be singing?
CONTINUOU S PERFECT have been + -ing + I had been singing I have been singing I will have been singing - I had not been singing I have not been singing I will not have beensinging? Had I been singing? Have I been singing? Will I have been singing?
The basic structure of tenses for regular verbs and irregular verbs is exactly the same (except to be). The only difference is that with regular verbs the past and past participle are always the same (worked, worked), while with irregular verbs the past and past participle are not always the same (sang, sung). But the structure is the same! It will help you a great deal to really understand that. 10 • I.7 Basic Tenses: Be This page shows the basic tenses with the verb be.
It includes the affirmative or positive form (+), the negative form (-) and the interrogative or question form (?). The basic structure is: positive (+): subject + auxiliary verb + main verb negative (-): subject + auxiliary verb + not + main verb question (?): auxiliary verb + subject + main verb But for simple past and simple present tenses, the structure is not the same. In fact, it's even easier. There is no auxiliary verb. Here is the structure: positive (+): subject + main verb negative (-): subject + main verb + not question (?): main verb + subject These are the forms of the main verb be that we use to construct the tenses: base past simple past participle present participle present simple be was, were been being am, are, is In the following table, we see be conjugated for 12 basic tenses.
11 past present future SIMPLE present simple or past simple (except future: will + be) + I was I am I will be - I was not I am not I will not be? SIMPLE PERFECT have + been + I had been I have been I will have been - I had not been I have not been I will not have been?
Will I have been? CONTINUOUS be + being + I was being I am being I will be being - I was not being I am not being I will not be being?
Will I be being? CONTINUOUS PERFECT have been + being + I had been being I have been being I will have been being - I had not beenbeing I have not beenbeing I will not have beenbeing? Had I been being? Have I been being? Will I have been being?