Palladio Four Books Of Architecture Pdf Portfolio

Express Helpline- Get answer of your question fast from real experts. White Paper a Palladio. This action might not be possible to undo. To celebrate the exhibition in the Architecture Gallery. The RIBA Journal is the official publication of the Royal Institute of British Architects. The PDF file containing this unit study is. Although additional books and library materials. We recommend that children.
Some of the gardens on the property Monticello was the primary of, the third, who began designing and building Monticello at age 26 after inheriting land from his father. Located just outside,, in the region, the plantation was originally 5,000 acres (20 km 2), with Jefferson using slaves for extensive cultivation of tobacco and mixed crops, later shifting from tobacco cultivation to wheat in response to changing markets. Due to its architectural and historic significance, the property has been designated a. In 1987 Monticello and the nearby, also designed by Jefferson, were together designated a. The current features a depiction of Monticello on its reverse side.
Jefferson designed the using design principles described by and reworking the design through much of his presidency to include design elements popular in late 18th-century Europe and integrating numerous of his own design solutions. Situated on the summit of an 850-foot (260 m)-high peak in the south of the Rivanna Gap, the name Monticello derives from the for 'little mount'. Along a prominent lane adjacent to the house, Mulberry Row, the plantation came to include numerous outbuildings for specialized functions, e. Russell Bernard Research Methods In Anthropology Pdf Files. g., a nailery; quarters for domestic slaves; gardens for flowers, produce, and Jefferson's experiments in plant breeding—along with tobacco fields and mixed crops. Cabins for field slaves were farther from the mansion. At Jefferson's direction, he was buried on the grounds, in an area now designated as the Monticello Cemetery.
The cemetery is owned by the, a society of his descendants through. After Jefferson's death, his daughter sold the property. In 1834 it was bought by, a commodore in the U.S. Navy, who admired Jefferson and spent his own money to preserve the property.
His nephew took over the property in 1879; he also invested considerable money to restore and preserve it. In 1923, Monroe Levy sold it to the (TJF), which operates it as a house museum and educational institution.
Contents • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Design and building [ ] Jefferson's home was built to serve as a, which ultimately took on the architectural form of a. It has many architectural antecedents, but Jefferson went beyond them to create something very much his own. He consciously sought to create a new architecture for a new nation. Work began on what historians would subsequently refer to as 'the first Monticello' in 1768, on a plantation of 5,000 acres (2,000 hectares). Jefferson moved into the South Pavilion (an outbuilding) in 1770, where his new wife joined him in 1772.
Jefferson continued work on his original design, but how much was completed is of some dispute. In constructing and later reconstructing his home, Jefferson used both free workers and enslaved laborers. After his wife's death in 1782, Jefferson left Monticello in 1784 to serve as Minister of the United States to France. During his several years in Europe, he had an opportunity to see some of the classical buildings with which he had become acquainted from his reading, as well as to discover the 'modern' trends in French architecture that were then fashionable in Paris. His decision to remodel his own home may date from this period.
In 1794, following his service as the first U.S. Secretary of State (1790–1793), Jefferson began rebuilding his house based on the ideas he had acquired in Europe. The remodeling continued throughout most of his presidency (1801–1809). Although generally completed by 1809, Jefferson continued work on the present structure until his death in 1826. Under the dome Jefferson added a center hallway and a parallel set of rooms to the structure, more than doubling its area. He removed the second full-height story from the original house and replaced it with a bedroom floor.
The interior is centered on two large rooms, which served as an entrance-hall-museum, where Jefferson displayed his scientific interests, and a music-sitting room. The most dramatic element of the new design was an octagonal, which he placed above the west front of the building in place of a second-story portico. The room inside the dome was described by a visitor as 'a noble and beautiful apartment,' but it was rarely used—perhaps because it was hot in summer and cold in winter, or because it could only be reached by climbing a steep and very narrow flight of stairs. The dome room has now been restored to its appearance during Jefferson's lifetime, with 'Mars ' walls and a painted green floor. Summertime temperatures are high in the region, with indoor temperatures of around 100 °F (38 °C). Jefferson himself is known to have been interested in Roman and Renaissance texts about ancient temperature-control techniques such as ground-cooled air and heated floors. Monticello's large central hall and aligned windows were designed to allow a cooling air-current to pass through the house, and the octagonal cupola draws hot air up and out.
Moderate air conditioning, designed to avoid the harm to the house and its contents that would be caused by major modifications and large temperature differentials, was installed in the house, a tourist attraction, in the late twentieth century. Before Jefferson's death, Monticello had begun to show signs of disrepair. The attention Jefferson's demanded, and family problems, diverted his focus. The most important reason for the mansion's deterioration was his accumulating debts.
In the last few years of Jefferson's life, much went without repair in Monticello. A witness,, who visited Jefferson in 1824, thought it run down. Java The Installer Cannot Proceed With The Current Internet Connection Proxy Settings.
He said, 'His house is rather old and going to decay; appearances about his yard and hill are rather slovenly. It commands an extensive prospect but it being a misty cloudy day, I could see but little of the surrounding scenery.'
History [ ] After Jefferson died on July 4, 1826, his only official surviving daughter,, inherited Monticello. The estate was encumbered with debt and Martha Randolph had financial problems in her own family because of her husband's. In 1831 she sold Monticello to James Turner Barclay, a local.
Barclay sold it in 1834 to, the first Commodore (equivalent to today's admiral) in the. A fifth-generation American whose family first settled in, Levy greatly admired Jefferson and used his private funds to repair, restore and preserve the house. The government seized the house as enemy property at the outset of the and sold it to Confederate officer. Levy's recovered the property after the war. Levy's heirs argued over his estate, but their lawsuits were settled in 1879, when Uriah Levy's nephew,, a prominent lawyer, and stock speculator (and later ), bought out the other heirs for $10,050, and took control of Monticello. Like his uncle, Jefferson Levy commissioned repairs, restoration and preservation of the grounds and house, which had been deteriorating seriously while the lawsuits wound their way through the courts in New York and Virginia. Together, the Levys preserved Monticello for nearly 100 years.
Monticello depicted on the reverse of the 1953. Note the two 'Levy lions' on either side of the entrance. The lions, placed there by Jefferson Levy, were removed in 1923 when the Thomas Jefferson Foundation purchased the house. In 1923, a private, the, purchased the house from Jefferson Levy with funds raised by Theodore Fred Kuper and others. They managed additional restoration under architects including and. Since that time, other restoration has been performed at Monticello.
[ ] The Foundation operates Monticello and its grounds as a house and educational institution. Visitors can wander the grounds, as well as tour rooms in the cellar and ground floor. More expensive tour pass options include sunset hours, as well as tours of the second floor and the third floor including the iconic dome. Monticello is a. It is the only private home in the United States to be designated a. Included in that designation are the original grounds and buildings of Jefferson's. From 1989 to 1992, a team of architects from the (HABS) of the United States created a collection of measured drawings of Monticello.
These drawings are held by the. Among Jefferson's other designs are, his private retreat near (which he intended for his daughter Maria, who died at age 25); the University of Virginia, and the in. [ ] Decoration and furnishings [ ] Much of Monticello's interior decoration reflects the personal ideas and ideals of Jefferson. In a time before refrigeration, Jefferson had the pond stocked with fish, to be available on demand.
The original main entrance is through the on the east front. The ceiling of this portico incorporates a wind plate connected to a, showing the direction of the wind.
A large face on the external east-facing wall has only an hour hand since Jefferson thought this was accurate enough for slaves. The clock reflects the time shown on the 'Great Clock', designed by Jefferson, in the entrance hall. The entrance hall contains recreations of items collected by on the cross-country expedition commissioned by Jefferson to explore the Louisiana Purchase. Jefferson had the floorcloth painted a 'true grass green' upon the recommendation of artist, so that Jefferson's 'essay in architecture' could invite the spirit of the outdoors into the house.
[ ] The south wing includes Jefferson's private suite of rooms. The library holds many books from his third collection.
His first library was burned in an accidental plantation fire, and he 'ceded' (or sold) his second library in 1815 to the to replace the books lost when the British burned the Capitol in 1814. This second library formed the nucleus of the. As 'larger than life' as Monticello seems, the house has approximately 11,000 square feet (1,000 m 2) of living space. Jefferson considered much furniture to be a waste of space, so the table was erected only at mealtimes, and beds were built into cut into thick walls that contain storage space. Jefferson's bed opens to two sides: to his cabinet (study) and to his bedroom (dressing room). The west front ( illustration) gives the impression of a villa of modest proportions, with a lower floor disguised in the hillside.
[ ] The north wing includes two guest bedrooms and the dining room. It has a incorporated into the fireplace, as well as dumbwaiters (shelved tables on casters) and a pivoting serving door with shelves. Slave quarters on Mulberry Row [ ] Jefferson located one set of his slaves' quarters on Mulberry Row, a one-thousand foot road of slave, service, and industrial structures. Mulberry Row was situated three hundred feet (91 m) south of Monticello, with the slave quarters facing the Jefferson mansion. These slave cabins were occupied by the slaves who worked in the mansion or in Jefferson's manufacturing ventures, and not by those who labored in the fields. Plaque at Monticello about slave labor of the site shows that the rooms of the slave cabins were much larger in the 1770s than in the 1790s. Researchers disagree as to whether this indicates that more slaves were crowded into a smaller spaces, or that fewer people lived in the smaller spaces.
Earlier slave houses had a two-room plan, one family per room, with a single, shared doorway to the outside. But from the 1790s on, all rooms/families had independent doorways. Most of the cabins are free-standing, single-room structures. By the time of Jefferson's death, some slave families had labored and lived for four generations at Monticello. Six families and their descendants were featured in the exhibit, Slavery at Jefferson's Monticello: Paradox of Liberty (January to October 2012) at the 's, which also examines Jefferson as slaveholder.
Developed as a collaboration between the and Monticello, it is the first exhibit on the national mall to address these issues. In February 2012, Monticello opened a new outdoor exhibit on its grounds: Landscape of Slavery: Mulberry Row at Monticello, to convey more about the lives of the hundreds of slaves who lived and worked at the plantation. Outbuildings and plantation [ ]. Jefferson grave at Monticello The main house was augmented by small outlying pavilions to the north and south.
A row of outbuildings (dairy, a washhouse, store houses, a small nail factory, a joinery etc.) and 's quarters (), known as Mulberry Row, lay nearby to the south. A stone weaver's cottage survives, as does the tall chimney of the joinery, and the foundations of other buildings. A cabin on Mulberry Row was, for a time, the home of, the household slave who is widely believed to have had a 38-year relationship with the widower Jefferson and to have borne six children by him, four of whom survived to adulthood. The genealogist Helen F.M. Leary concluded that 'the chain of evidence securely fastens Sally Hemings's children to their father, Thomas Jefferson.' Later Hemings lived in a room in the 'south dependency' below the main house. On the slope below Mulberry Row, slaves maintained an extensive vegetable garden for Jefferson and the main house.
In addition to growing flowers for display and producing crops for eating, Jefferson used the for experimenting with different species. The house was the center of a plantation of 5,000 acres (2,000 ha) tended by some 150 slaves. There are also two houses included in the whole. Programming [ ] In recent decades, the TJF has created programs to more fully interpret the lives of slaves at Monticello. Beginning in 1993, researchers interviewed descendants of Monticello slaves for the Getting Word Project, a collection of oral history that provided much new insight into the lives of slaves at Monticello and their descendants. (Among findings were that no slaves adopted Jefferson as a surname, but many had their own surnames as early as the 18th century.
) New research, publications and training for guides has been added since 2000, when the Foundation's Research Committee concluded it was highly likely that Jefferson had fathered Sally Hemings' children. Some of Mulberry Row has been designated as sites, where excavations and analysis are revealing much about slave life at the plantation. In the winter of 2000–2001, the slave burial ground at Monticello was discovered.
In the fall of 2001, the Thomas Jefferson Foundation held a commemoration of the burial ground, in which the names of known slaves of Monticello were read aloud. Additional archeological work is providing information about burial practices. In 2003 Monticello welcomed a reunion of descendants of Jefferson from both the Wayles' and Hemings' sides of the family. It was organized by the descendants, who have created a new group called the Monticello Community.
Additional and larger reunions have been held. Land purchase [ ] In 2004, the trustees acquired Mountaintop Farm (also known locally as Patterson's or Brown's Mountain), the only property that overlooks Monticello. Jefferson had called the taller mountain Montalto. To prevent development of new homes on the site, the trustees spent $15 million to purchase the property. Jefferson had owned it as part of his plantation, but it was sold off after his death. In the 20th-century, its farmhouses were divided into apartments for many students.
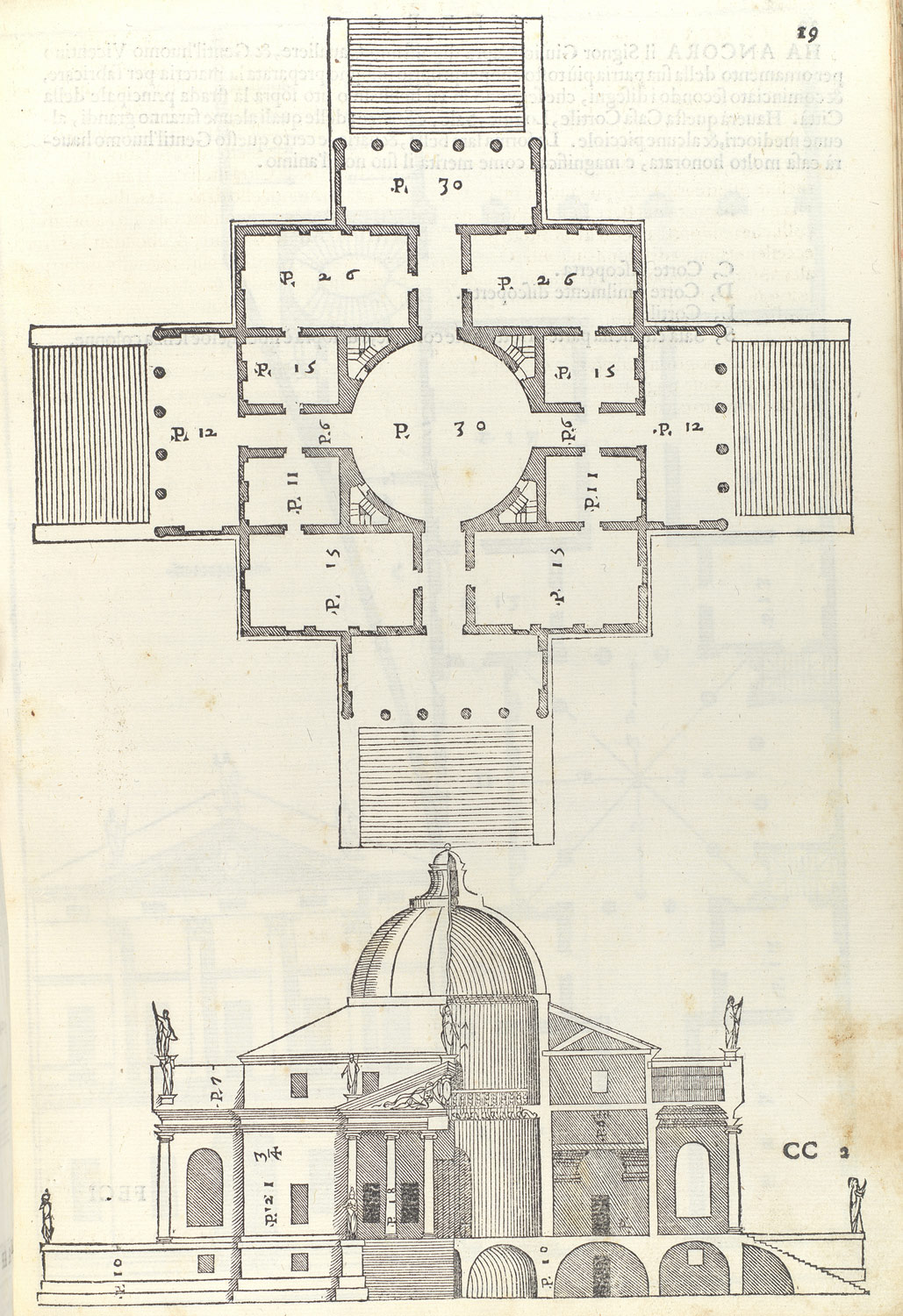
The officials at Monticello had long considered the property an eyesore, and planned to acquire it when it became available. Architecture [ ]. Main article: The house is similar in appearance to, a Neoclassical house inspired by the architect Andrea Palladio built in 1726-9 in. Representation in other media [ ] Monticello was featured in 's production, Guide to Historic Homes of America, in a tour which included Honeymoon Cottage and the Dome Room, which is open to the public during a limited number of tours each year. Replicas [ ] In 2014, constructed a 10,000 square foot replica of Monticello in. It can be seen on Rte 186 also known as Hall Hill Rd. A replica of Monticello was constructed in.
[ ] The entrance pavilion of the at Annapolis is modeled on Monticello. [ ] Chamberlin Hall at in, built in 1962 and modeled on Monticello, serves as the location of the Academy's Middle School. Completed in August 2015, built one of the largest replicas of Monticello, including its entry halls and a dome room. Approximately 23,000 square feet, it is the home of the Gary Cook School of Leadership, as well as the University Chancellor's offices. On April 13, 1956, the U.S. Post Office issued a honoring Monticello. Monticello's image has appeared on U.S.
Currency and postage stamps. An image of the west front of Monticello by has been featured on the of the since 1938 (with a brief interruption in 2004 and 2005, when designs of the series appeared instead). It was also used as the title for the 2015 play, which centred on his life. Monticello also appeared on the reverse of the from 1928 to 1966, when the bill was discontinued. The current was introduced in 1976 and retains Jefferson's portrait on the obverse but replaced Monticello on the reverse with an engraved modified reproduction of 's. The gift shop at Monticello hands out two-dollar bills as change. Gallery [ ] •.
• (2006-03-15).. National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service. National Historic Landmark summary listing. National Park Service. Retrieved 2008-06-27.
Virginia Department of Historic Resources. Retrieved 2015-11-16. •, Retrieved December 28, 2010. • ^ SAH Archipedia, eds. Gabrielle Esperdy and Karen Kingsley, Charlottesville: UVaP, 2012.
Accessed 2013-03-16. National Park Service, US Dept of the Interior. Retrieved 30 April 2011. • Kern, Chris.. Retrieved 2009-07-10. • • MARYLOU TOUSIGNANT (17 May 1998).. Los Angeles Times.
Retrieved 7 August 2016. Popular Science. October 2000. • Peden, William (1949).. The William and Mary Quarterly. 6 (4): 631–636.. • Marc Leepson, Saving Monticello: The Levy Family's Epic Quest to Rescue the House That Jefferson Built (New York: Free Press, 2001, p.
94 • Leepson. Saving Monticello. University of Virginia Press.. • Fleming, Thomas. 'The Jew Who Helped Save Monticello', The Jewish Digest, February 1974: 43–49. Retrieved 2015-07-28.
Library of Congress. Retrieved 2017-01-19. Retrieved 2010-07-09.
Retrieved 2016-09-19. Retrieved 2010-07-09. • - Monticello website •. Retrieved 2010-07-09. • Whiffen, Marcus & Koeper, Frederick (1981). American Architecture, 1607–1976. MIT Press, Cambridge, Mass P.105 • Self, R.
L., & Stein, S. The Collaboration of Thomas Jefferson and John Hemings: Furniture Attributed to the Monticello Joinery.
Winterthur Portfolio, 33(4), 231-248. Retrieved 2011-03-26. • • 2012-05-06 at • Helen F.M. Leary, 'Sally Hemings's Children: A Genealogical Analysis of the Evidence', National Genealogical Society Quarterly, Vol. 3, September 2001, p. 207 (165-207) •, Plantation and Slavery, Monticello, accessed 21 March 2011 •, Plantation and Slavery, Monticello, accessed 21 March 2011 •, Genealogy, MSNBC, 13 July 2003, accessed 1 March 2011 •.
• Miranda Zhang (October 14, 2014).. • • • Scotts U.S. Stamp Catalogue External links [ ] about Monticello • • • Wikimedia Commons has media related to. • • •, private lineage society of Jefferson descendants • Popular Mechanics, August 1954, pp. 97–103/212.
•, from 's, broadcast from Monticello, April 2, 1999 • at the (HABS).
En.wikipedia.org I quattro libri dell'architettura - Wikipedia 705 × 1063 - 313k - jpg amazon.com The Four Books of Architecture (Dover Architecture): Andrea. 383 × 499 - 50k - jpg palladiancenter.org CPSA Palladio and his Books 198 × 292 - 70k - jpg en.wikipedia.org Andrea Palladio - Wikipedia 170 × 256 - 20k - jpg commons.wikimedia.org File:Frontispiece Campbell's edition of Palladio's First Book of. 750 × 1160 - 404k - jpg metmuseum.org Andrea Palladio I quattro libri dell'architettura di Andrea.
2259 × 3225 - 2463k - jpg pinterest.co.uk facsimilium: Quattro Libri dell'Architettura (The Four Books of. 1600 × 1135 - 629k - jpg facsimilium.blogspot.com facsimilium: September 2011 1600 × 1149 - 652k - jpg abebooks.com Four Books Architecture by Palladio, First Edition - AbeBooks 300 × 477 - 21k - jpg blog.monticelloshop.org Book Recommendations 350 × 350 - 49k - gif queertango.us Architecture Photography Dissertation - Interior Design 800 × 1280 - 376k - jpg queertango.us Architecture Photography Dissertation - Interior Design 800 × 1279 - 217k - jpg pinterest.com 131 best Michael Graves style images on Pinterest Architecture. 640 × 755 - 101k - jpg metmuseum.org The Rediscovery of Classical Antiquity Essay Heilbrunn. 1029 × 1500 - 388k - jpg pinterest.com A classical architecture antique print from Palladio's ' Four Books. 1000 × 1000 - 118k - jpg amazon.com The Four Books on Architecture: Andrea Palladio, Richard Schofield. 349 × 500 - 16k - jpg pinterest.co.uk Conjectural reconstruction of the Baths of Agrippa, Andrea.
564 × 398 - 50k - jpg pinterest.com 90 best Architectural books images on Pinterest Walter o'brien. 318 × 475 - 41k - jpg pinterest.com 129 best Archiporn images on Pinterest Architecture, Villa. 530 × 836 - 76k - jpg pinterest.com Conjectural reconstruction of the Baths of Agrippa, Andrea.
236 × 362 - 19k - jpg.